Can nervousness impact the accuracy of a polygraph exam?
The short answer is no – anxiety cannot alter the outcome of a lie detector test conducted by a qualified examiner. Despite widespread misconception, polygraphs don’t measure mental stress levels. The technique is premised on an entirely different concept.
But while stress won’t affect the accuracy of a professionally administered polygraph evaluation, it can impact other dynamics like the test’s duration. Intense nervousness may necessitate more irrelevant questions to help the examinee relax.
If the feelings persist despite the examinee’s best efforts to calm down, an examiner might choose to cancel the test altogether. Read on as we explore the underlying causes of polygraph nervousness and why anxiety doesn’t indicate dishonesty.
Is Polygraph Nervousness A Sign Of Deception?
Anxiety during lie detector tests isn’t a sign of deception.
Polygraph examiners typically don’t make decisions based on examinees’ mental dispositions. Rather, they rely on physiological data recorded by the lie detector machine.
Simply put, a guilty polygraph examinee may develop anxiety for fear of failing the test. But so can an innocent subject.
Understanding the Science Behind Lying
Lying refers to the deliberate act of telling a falsehood. It can assume multiple forms, from exaggerating facts to misrepresenting them altogether.
Lying is a cognitive process. That means it’s principally controlled by the brain and central nervous system (CNS).
While various regions of the brain are involved in suppressing the truth, the prefrontal cortex plays the biggest role.

What Do Polygraphs Measure?
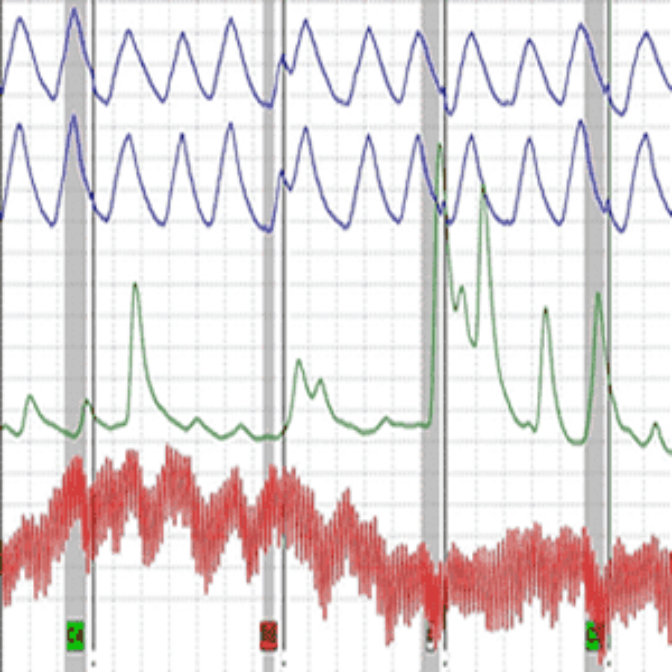
Contrary to popular belief, polygraph machines don’t discern lying directly. Instead, they measure certain physiological reactions synonymous with deception.
Research has shown that lying elevates the autonomic nervous system (ANS). This causes a spike in various ANS-controlled functions, particularly heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and skin conductivity.
Relationship Between Lying and Nervousness
Lying activates the autonomic nervous system, the same system responsible for regulating anxiety. ANS controls nervousness through its sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic nervous system helps initiate the “fight-or-flight” response, while the parasympathetic system promotes “rest and digest.” The two ANS divisions cancel each other out.
Stress results from an imbalance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Why Isn’t Polygraph Anxiety a Sign of Deception
1. General Test Anxiety
Undergoing a polygraph test is inherently stressful. The experience is closely comparable to a public servant getting grilled on national television. While industry standards require lie detector tests to be conducted in private rooms, these exams retain the element of scrutiny.
Many people will become anxious at the mere act of getting questioned over a crime. That’s regardless of whether they’re guilty or innocent. Polygraph tests also involve attaching complex biofeedback sensors to an examinee’s body.
Unless the examinee was properly acclimatized to the process, these appendages can add an extra layer of anxiety.
2. Uncomfortable Environment
Polygraph tests often unfold in formal, investigating environments similar to those used for regular detective work. Getting subjected to such settings can trigger an anxious response.
Some examiners may also assume an overly formal demeanor. This only reinforces the perception that the examinee is being grilled, worsening their anxiety.
3. Insufficient Preparation
There’s a reason polygraph examiners should establish prior contact with an examinee ahead of each lie detector test, which all happens on the same day.
Besides obtaining the examinee’s consent, preliminary engagements also help prepare the individual for the exam.
An examiner will recommend the best foods to take and what to avoid. For instance, excess caffeine intake can wreak havoc on your cognitive functions and elevate your stress levels.
Other ways to prevent polygraph anxiety include;
- Avoiding certain medications, including antidepressants, ahead of the test
- Avoiding psychedelic compounds like marijuana
- Wearing comfortable clothing
- Maintaining an upright, confident posture
- Getting plenty of sleep and exercise the previous day
4. Fear of False Positives
Innocent examinees may develop polygraph anxiety for fear of false positives.
False positives occur when a lie detector test turns up a deceptive verdict on an otherwise innocent person. It contrasts with false negatives, which erroneously exonerate guilty individuals.
Note that anxiety cannot cause false positives or false negatives by and of itself. Regardless, the mere fear of failing the exam can trigger heightened stress.
5. Use of Pharmacological Countermeasures
When an innocent person undergoes a polygraph test, they’ll want to pull out every stop to prove their innocence. Unfortunately, that may include using countermeasures.
Polygraph countermeasures are attempts to manipulate lie detector tests. They include;
- Physical countermeasures, such as lip biting and fist clenching
- Mental countermeasures, such as blocking certain emotions
- Pharmacological countermeasures, such as using antidepressants
While an examinee may take antidepressants to calm down ahead of a lie detector test, these are found to be counterproductive. Certain drugs may elevate your stress levels rather than calm you down.

Wrap Up
Polygraphs are inherently anxious moments. The intense examination that characterizes lie detector tests can activate certain physiological responses, causing intense nervousness.
Even if an examinee is innocent, the fears of false positives can make them excessively jittery.
However, there’s no conclusive proof linking polygraph anxiety to deception. Neither can nervousness impact the outcome of a well-administered lie detector test.
To separate normal anxiety from deception-triggered stress, polygraphers should collect an examinee’s baseline data ahead of each test. Physiological reactions to in-test questions are measured against the baselines to infer truthfulness or deception.